Effective communication is pivotal for the business landscape. Companies compare Primary Rate Interface (PRI) and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) to find technologies that enhance communication while ensuring cost-efficiency and scalability. Understanding the applicability of these technologies is crucial for informed decision-making. The choice between PRI and SIP should consider specific communication needs, infrastructure, and future goals. Adopting a robust and scalable communication solution aligned with business objectives begins with understanding these technologies.
In this article, we’ll explore how PRI and SIP can be a game-changer in your call centre’s success, ensuring swift and satisfactory results.
Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
PRI is a telecommunication interface standard for carrying voice and data transmissions between a network and a user. It leverages physical copper wires to connect your business with the public switched telephone network (PSTN). This technology aggregates calls from national, regional, and local telephone operators, managing them through a private branch exchange (PBX) system. The significance of PRI lies in its reliability and compatibility with legacy telephony systems, making it a go-to choice for large organizations and enterprises.
The Primary Rate Interface (PRI) is a fascinating blend of traditional telephony and digital technology. At its core, PRI employs a T1 or E1 line, which are types of digital transmission systems commonly used in telecommunications. Let’s break down the technical aspects to understand how PRI functions.
T1 and E1 Lines: The Backbone of PRI
- T1 Line (North America): This line is structured to carry 24 channels. In the context of PRI, 23 of these channels are designated as B-channels (Bearer channels), and one as a D-channel (Delta channel). Each B-channel provides a bandwidth of 64 Kbps.
- E1 Line (Europe and other regions): Similar to T1, an E1 line in PRI configuration includes 30 B-channels and one D-channel. The key difference lies in the higher number of B-channels, offering expanded capacity.
Role of B-Channels and D-Channel
- B-Channels (Bearer Channels): These channels are the workhorses of PRI. Each B-channel can independently carry a voice call or data transmission. The key advantage here is the dedicated nature of these channels, ensuring consistent quality without interference from other transmissions.
- D-Channel (Delta Channel): Unlike the B-channels, the D-channel does not carry voice or data. Instead, its role is pivotal in controlling and managing the network. It handles signaling for establishing, maintaining, and terminating calls on the B-channels. This includes transferring caller ID information, dialing, and call routing instructions.
How PRI Integrates with Business Systems
- Seamless PBX Integration: Businesses often use Private Branch Exchange (PBX) systems to manage their internal telecommunications. PRI interfaces effortlessly with these systems, providing a robust gateway for external communication while maintaining internal efficiency.
- Direct Inward Dialing (DID): This feature is particularly beneficial for businesses as it allows external calls to bypass the operator and directly reach an extension. This streamlines communication and improves customer interaction.
Key Features of PRI
- Multiple Channels: PRI consists of 23 B channels and one D channel in North America, offering simultaneous connections for multiple users.
- Quality and Reliability: Offers superior voice quality and is less susceptible to outages and interruptions.
- Direct Inward Dialing (DID): Enables direct calling to extensions within an organization without a receptionist.
Requirements for PRI Implementation
To deploy PRI, businesses need PRI-compatible equipment, like a PRI gateway or a PBX with a PRI card. While PRI allows 23 simultaneous calls, its capability can be enhanced with additional PRI circuits to handle increased call volumes.

Brayan Carpio
“The technology aspect of NobelBiz stood out compared to the competition, and also the great team! All the way from onboarding to support to troubleshooting has been great throughout this journey!”
Pros and Cons: Understanding Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
Pros of PRI | Cons of PRI | ||
High-Quality Voice and Data Transmission With dedicated B-channels for each call, PRI ensures clear, high-quality transmission, free from common issues like latency and jitter. | Higher Initial Setup Cost Setting up PRI can be more expensive initially compared to other solutions like VoIP. | ||
Scalability and Flexibility PRI allows for easy expansion with additional circuits, making it suitable for growing businesses. | Dependence on Physical Infrastructure PRI requires physical T1/E1 lines, which can be a limitation in areas lacking this infrastructure. | ||
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) This feature enables direct calling to extensions, improving customer experience and internal efficiency. | Less Flexibility in Location Being tied to physical lines, PRI systems are less adaptable to remote or flexible working environments. | ||
Compatibility with PBX Systems PRI seamlessly interfaces with PBX systems, aiding in effective communication management. | Potential for Underutilization If the capacity of the B-channels is not fully utilized, it can lead to inefficiencies in cost and resource allocation. | ||
Security and Reliability PRI offers secure and consistent communication, crucial for handling sensitive information. |
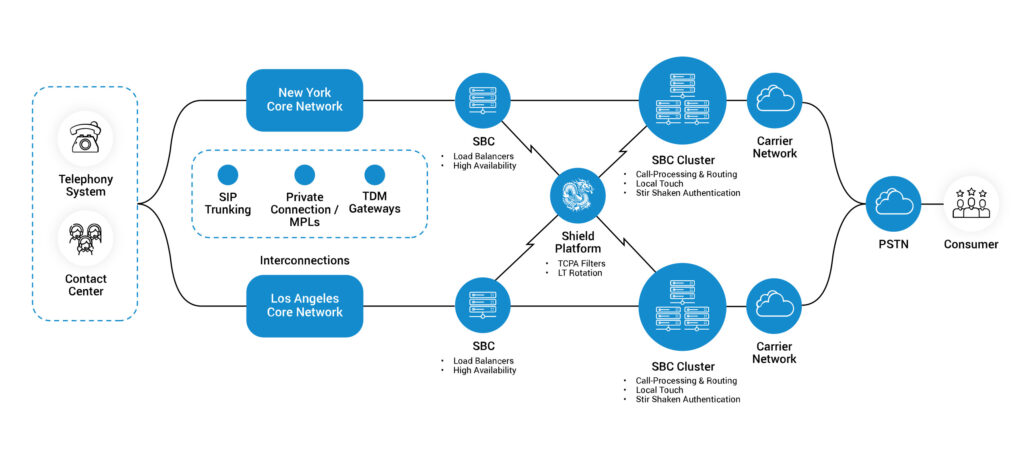
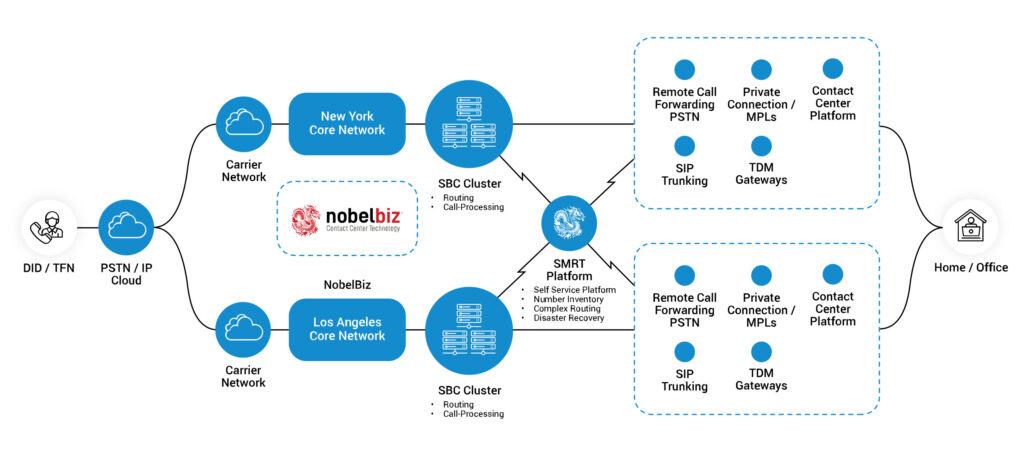
Nobelbiz’s voice infrastructure enhances the use of PRI and SIP in modern telecommunications.
Our network supports a seamless integration of both technologies, providing a robust and adaptable solution for businesses. With a focus on high-quality communication and scalability, Nobelbiz tailors its services to meet diverse business needs, whether it’s the security and reliability of PRI or the flexibility and efficiency of SIP.
This integration ensures that businesses can leverage the best of both worlds in telecommunications. For more information, you visit our voice infrastructure page.
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP): Flexibility and Scalability
Session Initiation Protocol, on the other hand, is a signaling protocol used for initiating, maintaining, and terminating real-time sessions. It is highly adaptable and scalable, making it a popular choice for modern VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) systems.
SIP connects your IP PBX to the internet, facilitating calls over the Internet. It stands out for its ability to consolidate multiple communication channels into a single virtual connection, effectively using resources while providing connection to a telephone network.
SIP is a specific protocol enabling Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), making it a critical component of modern IP phone communication systems.
SIP Operation: Breakdown of how it works
The operation of SIP involves several key components, which include User Agents, Proxy Servers, Registrar Servers, and Redirect Servers. These elements work together to ensure efficient and reliable communication.
- User Agents: Clients that initiate SIP requests.
- Proxy Servers: Route requests to the user’s current location, authenticate and authorize users for services, implement provider call-routing policies, and provide features to users.
- Registrar Servers: Responsible for keeping a record of users’ locations.
- Redirect Servers: Provide information about a callee’s new location to the caller.
SIP Messages and Response Codes
SIP utilizes request and response messages to control multimedia communication sessions. The common SIP requests include INVITE, ACK, BYE, CANCEL, and REGISTER. SIP responses are categorized into six classes, from 1xx to 6xx, indicating different levels of success or failure of the request.
Key Features of SIP:
- Flexibility: Easily integrates with various digital communication tools and supports voice, video, and messaging.
- Scalability: Can scale up or down based on the business needs, making it cost-effective.
- Mobility: Allows users to connect from anywhere, fostering a mobile and remote workforce.
Requirements for SIP Trunking
Transitioning to SIP trunking involves virtualizing your physical infrastructure. Necessary components include an Internet connection, SIP-compatible PBX (or IP PBX), and VoIP phones or adapters for traditional phones.

Brad Dashnaw
”Their software is easy to use, easy to implement, and able to be integrated with our own platforms. We were able to train people easily, and deploy it to their computers in their home offices to keep productivity going!”
SIP Trunking Advantages | SIP Trunking Disadvantages |
Cost Efficiency Significantly reduces call costs, particularly for long-distance and international calls, by utilizing internet protocols. | Dependence on Internet Quality Call quality and reliability are directly tied to internet connectivity, with potential issues in case of poor or unstable connections. |
Scalability and Flexibility Allows businesses to easily adjust the number of channels according to their changing needs, offering a scalable solution for growth or downsizing. | Technical Complexity Requires technical expertise for setup and maintenance, which can be a challenge for businesses without dedicated IT staff. |
Enhanced Features Provides advanced communication features like call forwarding, voicemail to email, and automatic call distribution, enhancing business communication capabilities. | Security Concerns Being internet-based, it is susceptible to cyber threats, necessitating strong security measures. |
Integration with Existing Systems Can be integrated with existing VoIP systems and software, facilitating unified communications. | Potential Compatibility Issues May face compatibility challenges with older, traditional telephony equipment or systems. |
Business Continuity Enables quick re-routing of calls in case of emergencies or outages, ensuring consistent communication. | Regulatory and Compliance Issues May need to navigate varying telecommunications regulations, which can be complex, especially in different geographic locations. |
Remote Connectivity Supports remote work and mobile connectivity, allowing employees to connect from anywhere with an internet connection. | Initial Investment May require an initial investment in compatible hardware or upgrades to existing infrastructure. |
Comparing PRI and SIP: A Head-to-Head Overview
When comparing PRI and SIP, several factors come into play:
- Cost-Effectiveness: SIP generally offers lower operational costs compared to PRI.
- Scalability: SIP trunking is highly scalable, contrary to the limited scalability of PRI.
- Flexibility: SIP provides flexibility for on-premises and cloud-hosted solutions, whereas PRI is limited to on-premises.
- Hardware Requirements: SIP is less demanding in terms of hardware compared to PRI, which requires on-premises hardware.
Comparative Analysis: PRI vs. SIP
Feature | PRI | SIP |
Technology | Digital circuit-switched | Packet-switched, IP-based |
Scalability | Fixed number of channels | Easily scalable with business needs |
Flexibility | Limited to physical connections | High, supports remote and mobile users |
Cost | Generally higher due to hardware | Lower, uses existing internet infrastructure |
Implementation | Requires specific hardware | More straightforward, software-based |
Transitioning from PRI to SIP
For businesses considering a shift from PRI to SIP, the process involves:
- Assessment and Planning: Evaluate your voice and data usage and network compatibility with SIP.
- Selecting a SIP Service Provider: Choose a provider that balances cost, reliability, and support.
- Implementation: Train IT staff for migration and manage the porting of existing numbers to the new SIP service.
- Post-Migration Support: Establish a clear support agreement with the provider for ongoing assistance.
Summing up: Embracing Future-Ready Communication Solutions
In conclusion, both PRI and SIP have their unique strengths and limitations.
While PRI is renowned for its reliability and traditional telephony system compatibility, SIP stands out for its scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility. The choice between PRI and SIP should be guided by the specific communication needs, infrastructure, and future goals of your business. Understanding these technologies is the first step towards adopting a communication solution that is robust, scalable, and aligned with your business objectives.
The NobelBiz Voice Carrier Network is one of the best VoIP Interconnected Providers in the industry, with multiple worldwide redundancies for uninterrupted uptime, delivering the best possible voice quality at a fair price. In addition, all the features and support processes were fine-tuned to maximize the efficiency, quality, and demands of voice traffic, both inbound and outbound
Nobelbiz offers a comprehensive range of telecommunication services that cater to the unique needs of your call center business.
Our focus on delivering high-quality, reliable, and scalable communication solutions aligns seamlessly with the demands of modern business communications. This approach enables businesses to effectively leverage the strengths of both PRI and SIP, ensuring a versatile and future-proof telecommunications infrastructure.
Get the Best Voice for Your Contact Center, contact us here!

Michael McGuire is a contact center industry expert with almost two decades of experience in the space. His experience includes roles as Director of Contact Center Digital Transformation at NobelBiz, and as Director of Operations at FLS Connect, managing multiple call centers. As President of Anomaly Squared and Targeted Metrics, Michael successfully transitioned companies into remote operations and significantly boosted revenues. With a strong background in customer service, leadership, strategic planning, and operations management, Michael excels in driving growth and innovation in the call center space.
Mike is also a proud Board Member for R.E.A.C.H Trade Group, promoting consumer protection and satisfaction and Co-host of the Off Skripted Podcast – a show about Life, Call Centers and everything in between.







